 |

OUR EARTH
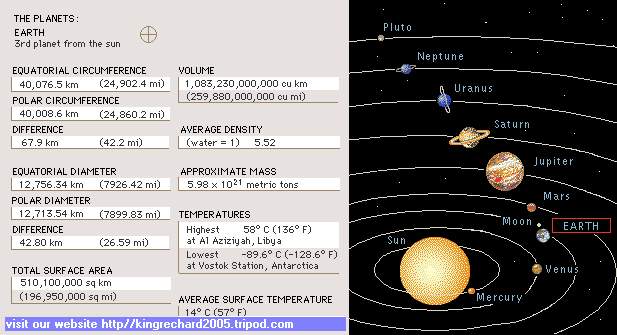
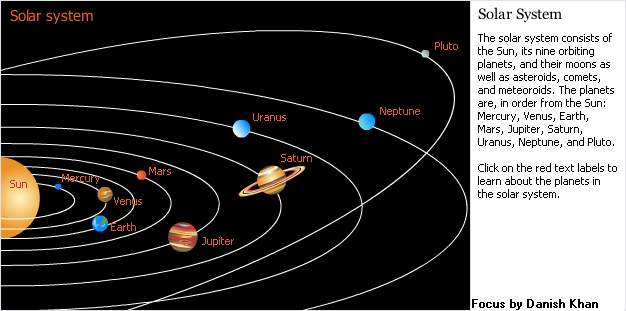
Earth (planet), one of the planets in the solar system, the third in distance from the sun and the fifth largest
of the planets in diameter. The mean distance of the earth from the sun is 149,503,000 km (92,897,000 mi). It is the only
planet known to support life, although some of the other planets have atmospheres and contain water.
Earth An oxygen-rich and protective atmosphere, moderate temperatures, abundant water, and a varied chemical composition
allow earth to support life, the only planet to do so. The slightly oblate planet is composed of rock and metal, which are
present in molten form beneath its surface. This photograph, taken by the Apollo 17 spacecraft in 1972, shows Arabia, the
African continent, and Antarctica (most of the white area near the bottom).NASA/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.
Expand
The
diameter of the earth, measured around the equator, is about 12756 km (7926 mi). The earth is not a perfect sphere but is
slightly oblate, or flattened at the poles. Because of this flattening, the diameter of the earth measured around the North
Pole and the South Pole is about 12713 km (7899 mi) — 43 km (27 mi) less than the equatorial diameter.
The earth consists of five parts: the first, the atmosphere, is gaseous; the second, the hydrosphere, is liquid; the
third, fourth, and fifth, the lithosphere, mantle, and core, are largely solid. The atmosphere is the gaseous envelope that
surrounds the solid body of the planet. Although it has a thickness of more than 1100 km (more than 700 mi), about half its
mass is concentrated in the lower 5.6 km (3.5 mi). The lithosphere, consisting mainly of the cold, rigid, rocky crust of the
earth, extends to depths of 100 km (60 mi). The hydrosphere is the layer of water that, in the form of the oceans, covers
approximately 70.8 percent of the surface of the earth. The mantle and core are the heavy interior of the earth, making up
most of the earth’s mass.
sidebar
SCIENTIFIC DISCOVERIES
Earth's Inner Core Spins Faster
The hydrosphere consists chiefly
of the oceans, but technically includes all water surfaces in the world, including inland seas, lakes, rivers, and underground
waters. The average depth of the oceans is 3794 m (12,447 ft), more than five times the average height of the continents.
The mass of the oceans is approximately 1.35 quintillion (1.35 × 1018) metric tons, or about 1/4400 of the total mass of the
earth.
The rocks of the lithosphere have an average density of 2.7 and are almost entirely made up of 11 elements, which together
account for about 99.5 percent of its mass. The most abundant is oxygen (about 46.60 percent of the total), followed by silicon
(about 27.72 percent), aluminum (8.13 percent), iron (5.0 percent), calcium (3.63 percent), sodium (2.83 percent), potassium
(2.59 percent), magnesium (2.09 percent) and titanium, hydrogen, and phosphorus (totaling less than 1 percent). In addition,
11 other elements are present in trace amounts of 0.1 to 0.02 percent. These elements, in order of abundance, are carbon,
manganese, sulfur, barium, chlorine, chromium, fluorine, zirconium, nickel, strontium, and vanadium. The elements are present
in the lithosphere almost entirely in the form of compounds rather than in their free state. These compounds exist almost
entirely in the crystalline state, so they are, by definition, minerals.
for further knoledge
|
